Malaria
What is Malaria?
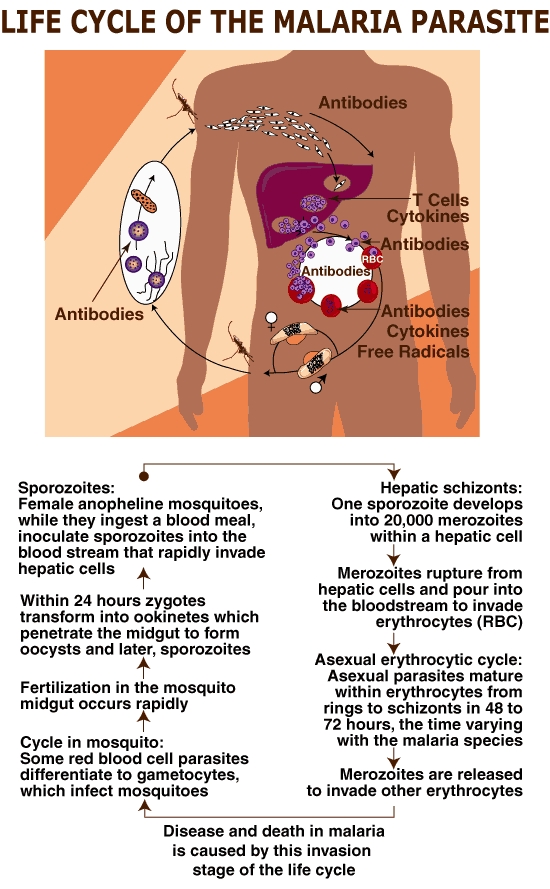
Malaria is a life-threatening parasitic disease transmitted by mosquitoes. It was once thought that the disease came from fetid marshes, hence the name mal aria (bad air). In 1880, scientists discovered the real cause of malaria: a one-cell parasite called plasmodium. Later they discovered that the parasite is transmitted from person to person through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito, which requires blood to nurture her eggs.
Causes and Risk Factors of Malaria
Malaria comes from being bitten by a mosquito carrying the malaria organism. Risk factors include traveling in areas in which such mosquitoes are found or, rarely, being bitten by a mosquito that has previously fed on an "imported" case of malaria (such that the case can occur in an area of the world where malaria is not endemic).Symptoms of Malaria
Malarial attacks present over 4 to 6 hours with shaking chills, high fever, and sweating, and are often associated with fatigue, headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, dry cough, muscle or joint pain, and back ache. The attacks may occur every other day or every third day.
Cerebral malaria and death can occur, sometimes within 24 hours, if the infection is caused by plasmodium falciparum.
Fever or other symptoms can develop in malaria as early as 8 days or as late as 60 days after exposure or stopping prophylaxis. For plasmodium vivax in temperate areas, the delay may be up to one year.Diagnosis of Malaria
Methods of diagnosis are:
- complete medical history of symptoms and travel
- physical examination
- blood tests, including thick and thin blood films, to identify the plasmodium species responsible for infectionTreatment of Malaria
Medical treatment should be sought immediately.The effectiveness of antimalarial drugs differs with different species of the parasite and with different stages of the parasite's life cycle. Your physician will determine the treatment plan most appropriate for your individual condition.
Drugs include chloroquine, mefloquine, primaquine, quinine, pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine (Fansidar), and doxycycline. Some plasmodium have developed resistance to certain medications, and therefore, alternative medications will be prescribed for you.Prevention of Malaria
No prophylactic regimen gives complete protection. Speak with your physician or local travel clinic to receive up to date information about the best malaria protection for you. Effectiveness of any given medication varies by the region of the world in which you plan to travel. Effectiveness also varies from year to year, so current information is essential.
Prevention is based on:
- evaluating the risk of exposure to infection
- preventing mosquito bites by using DEET mosquito repellant, bed nets, and clothing that covers most of the body
- chemoprophylaxis (preventive medications)Questions To Ask Your Doctor About Malaria
Are preventive measures necessary for the region of the world I'll be visiting?
Is this a high-risk area for malaria?
What drugs can be taken as a preventive measure?
What is the correct dosage?
When should the drug be started and stopped?
What other precautions should I take; repellents, clothes, nets?
What symptoms should I look for?
